[ad_1]
The euro hit a recent 20-year low towards the greenback on Friday after a benchmark survey of firms within the eurozone confirmed enterprise exercise suffered its largest contraction for 20 months, whereas worth pressures rose at their sharpest tempo since June.
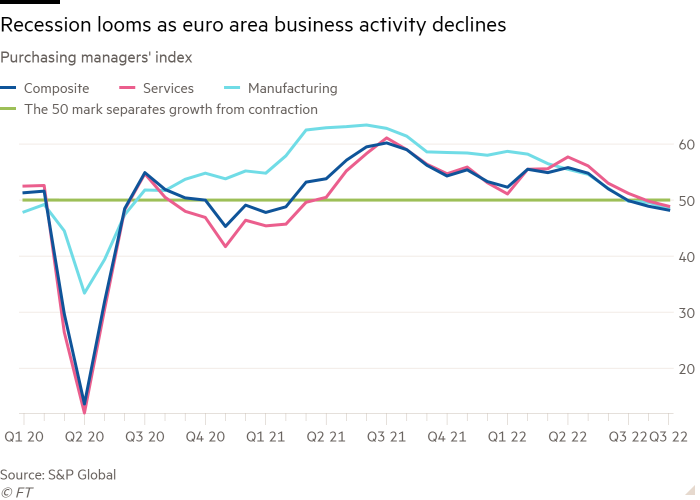
S&P World’s flash eurozone composite purchasing managers’ index — a key gauge of enterprise circumstances — fell 0.7 factors to 48.2, its lowest stage since January 2021 and the third consecutive month under the essential 50 mark that separates development from contraction.
The studying is the strongest proof but that the power disaster brought on by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has pushed the bloc into recession, together with sending inflation to file highs.
Eurozone bond and share costs plunged whereas the euro fell 0.9 per cent towards the greenback to 97.5 cents on Friday, its lowest stage since October 2002. Germany’s benchmark 10-year yield rose above 2 per cent for the primary time in 11 years, whereas the Dax-40 share index of blue-chip German firms fell 1.4 per cent to its lowest stage for nearly two years.
The slowdown in exercise underlines the problem dealing with the area’s financial policymakers, who’re anticipated to proceed elevating borrowing prices to struggle inflation despite the slowdown. “The stagflationary shock is actual, and it’s intensifying,” stated Claus Vistesen, an economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics.
European Central Financial institution has raised charges by 125 foundation factors to 0.75 per cent for the reason that begin of the summer time and is anticipated to extend borrowing prices once more at its October and December conferences.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is squeezing pure gasoline provides to Europe, inflicting file eurozone inflation, eroding family spending and hitting industrial manufacturing.
Deutsche Financial institution economists this week slashed their forecasts, saying the power disaster had already prompted the eurozone economic system to start out shrinking and predicting it might contract by a cumulative 3 per cent from the third quarter of this 12 months to the second quarter of 2023.
The PMI outcomes have been as anticipated by economists polled by Reuters — though Germany was weaker than France — underlining the challenges confronting the eurozone economic system after companies reported falling manufacturing facility output, declining new orders, hovering power costs and plummeting expectations.
“The survey’s forward-looking indicators level to a steepening financial decline for the eurozone within the fourth quarter, including to the probability of the area falling into recession,” stated Chris Williamson, chief enterprise economist at S&P World.
The 19-country bloc has accomplished higher than anticipated to date this 12 months, growing 0.8 per cent within the second quarter due to a restoration in tourism. Nonetheless, most economists suppose it’s already slowing sharply with a lot of them warning of a recession this winter.
The PMI survey painted a depressing image of enterprise circumstances on the finish of the third quarter, with producers reporting a fourth consecutive decline in factory output and “some proof of power market developments additionally limiting manufacturing capabilities”. Job development was unchanged from August, when it slowed to a 17-month low.
New orders for companies enterprise additionally fell at an elevated price as extra shoppers dealing with hovering power and meals prices stayed residence to save cash. Firms in all sectors reported the steepest enhance in prices since June, which led to an acceleration in development of costs charged for items and companies “as companies sought to guard margins”.
“Providers development within the eurozone is now slowing markedly in addition to inflation weighs additional on shopper buying energy,” stated Katharina Koenz, an economist at Oxford Economics. “And though the danger of power shortages over the winter has lowered considerably, it stays a key threat to the outlook.”
Provide chain constraints eased as supply occasions lengthened at their slowest tempo since October 2020. However Williamson stated excessive inflation was “not solely hitting demand but additionally limiting manufacturing manufacturing and repair sector exercise in some circumstances”.
A few of Europe’s largest power customers, from metal to chemical firms, are cutting back on manufacturing, and enterprise leaders are warning that hovering costs threat eroding the area’s competitiveness.
The PMI studying for Germany fell 1 level to 45.9, its lowest stage since Could 2020 shortly after the pandemic hit Europe, as a sharper than anticipated decline within the companies index added to a continued fall in manufacturing. “Germany will undergo greater than most over the approaching quarters as excessive power prices weigh on energy-intensive business in addition to family budgets,” stated Jack Allen-Reynolds, an economist at Capital Economics.
The French PMI studying rose 0.8 factors to a two-month excessive of 51.2, confounding expectations for a decline, as exercise was boosted by a rebound in companies.
Source link

