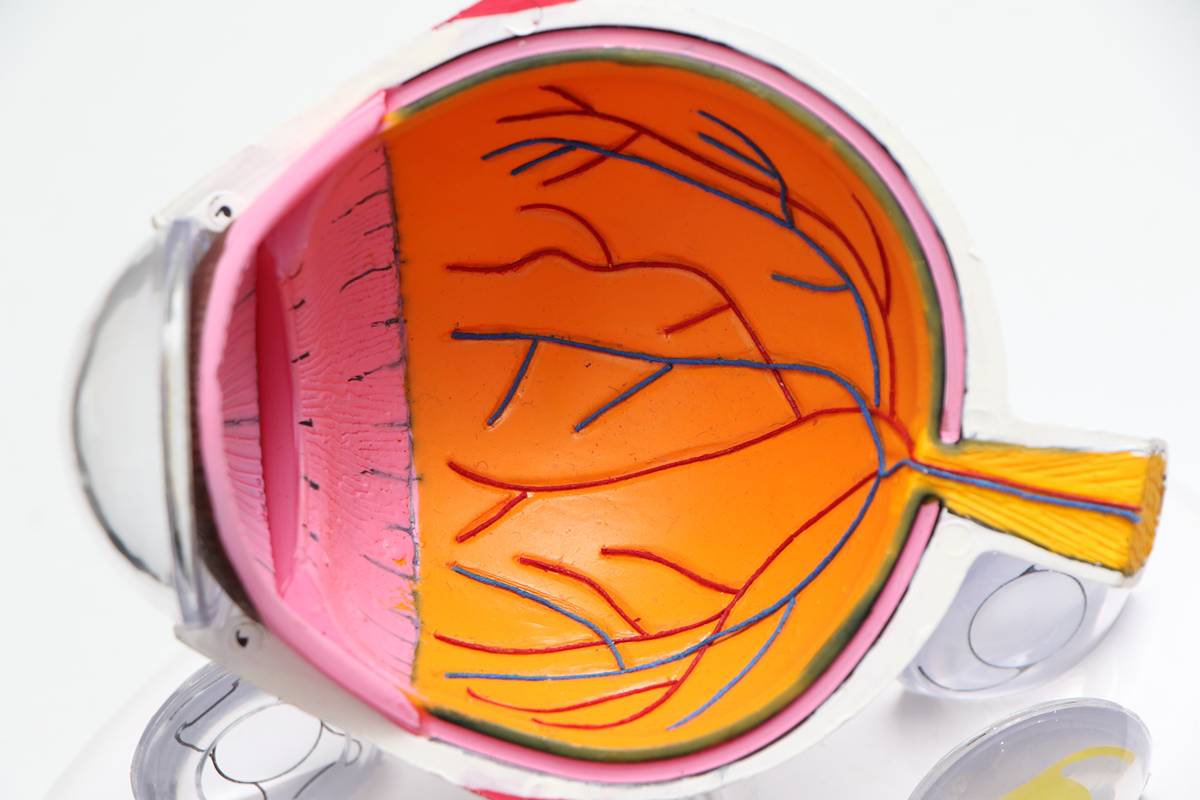
Human eyesight is commonly referred to as the human body’s most complex organ. It’s full of many different parts and is determined by all parts to work efficiently so as to have the best vision possible. Coming from all five senses, vision is among the most valued, and the quality of the vision is directly associated with the way the eye’s parts use each other.
Table of Contents
Basic Eye Body structure
The eye consists of 11 fundamental parts, all of which have an essential role in the vision procedure. The basic anatomy of the eyes includes the iris, cornea, pupil, lens, sclera, ciliary body, choroid, optic neural, macula, retina, and vitreous. Light enters through the cornea, which is the region of the sclera that is transparent. It provides attention with the power to focus and it is the part of the eye where lenses are placed. The color of your eyes, or the colored iris, is situated behind the cornea and it is visible only because the cornea is transparent.
The center of typically, the iris is the pupil, and that is the dark and spherical opening in the center. It includes control over how much gentle enters into the eye by simply dilating the size of the college student in conditions of darker light and constricting throughout conditions of bright light. Typically the lens also provides a number of focusing power within the eyesight and is located directly right behind the pupil. The shape of the lens changes to bring materials into focus-such as when you find yourself reading-and muscles contract which might be located in the ciliary human body. After a while, the muscles lose a chance to change shape and the contact becomes rigid which leads to some need for glasses.
Light pictures are converted into electric pulses by photosynthesis cells that define the retina. These electrical pulses then travel to the mind through the optic nerve. Good detailing is accomplished by the actual macula, which is a specialized region that is located in the center of the actual retina. The clarity associated with vision is determined by a combination of aspects: the length of the eye and the concentrating power of both the lens and also the cornea. Vision is clear in case these three factors go perfectly together; when they will not, this creates vision complications.
Sclera
The sclera, often known as the white part of the vision, is the protector of considerably more sensitive parts of the inner vision, such as the choroid and the retina. Most of the depth of the sclera is 0. 03-inch dense, but it is no more than zero. 01-inch thick where the immediate eye muscles connect. You will discover six muscles in each eye that control often the movements, but four are usually referred to as the straight-eye muscle tissues. The sclera is nourished with nutrients and air through blood vessels located in the particular episclera, which is located on the surface of the sclera.
Choroid
The choroid provides the retina with nutrients of nutrients and air through a network of arteries. It is located within the sclera and is responsible for providing the particular anterior part of the optic sensors as well as the macula with the blood circulation they depend on. When there is a great abnormal growth of blood vessels, a condition called macular weakening occurs, beginning in the choroid and going to the retina over the Bruch’s Membrane. Because of a sluggish structure, this causes edemas due to the bleeding or rupturing of the weakened vessels.
Retina
The retina is in the backside of the eyeball and is often the light-sensitive tissue that contains two different types of light receptors: cones in addition to rods. The cones commonly absorb the stronger light source and are color-sensitive, located in often the retina’s center. The fishing rod absorbs black and white in delicate light and is next to often the fovea. Retinal detachment, as well as emotional retinae, is a critical eye condition that creates symptoms such as light sensations or vision loss that will lead to permanent vision damage if left untreated.
Eyes
The iris has handled over how much light makes its way into the eye; the muscles in the iris sphincter with a written agreement with strong light and may dilate with dim mild. The diameter of the eyes expands when focusing on a physical object far away and narrows if focusing on near objects-this is named the accommodation reflex. A person’s vision color is direct regards to the type and amount of hues in a person’s iris. Environmentally friendly is the least common shade while brown is the most frequent.
Cornea
The cornea addresses the anterior chamber, the particular pupil, and the iris. It truly is transparent and contains two-thirds as well as 40 of the 60 diopters in the eye. It is given nutrients and oxygen by tear fluid instead of capillaries, which explains why it is so apparent. Blood vessels can appear in often the cornea though if there is oxygen deficiency which can come about from overusing contact lenses. This tends to cause partial vision decline if the vessels grow crowded to the center. Surgical procedures can be to correct eye conditions with the cornea such as astigmatism, hyperopia, and myopia.
Pupil
Often the pupil is the hole in the eye that absorbs important parts of light, which is the explanation it is black. When they turn up red in pictures, it can be due to the reflection of the retina.
Vitreous Body
This main eye is located behind often the lens and fills a person’s vision with a clear and gel-like substance. The vitreous physique shrinks as you get older and will detach from the retina because the body decreases in size. Vitreous body detachment is generally not just a dangerous condition but can be dangerous if it drags over the retina.
Lens
One-third of the eye’s diopters obtain their particular power in the lens even though the remainder is in the cornea. The particular lens is the part of the attention that allows you to change focus according to the distance of an object whether it be across the room or immediately in front of your face. It is mounted on zonula threads which are mounted on the ciliary body.
While focusing on a near subject, the ciliary body deals, which allows the zonula strings to loosen and the contact lens to increase its acuity by means of thickening in diameter even though contracting. Cataracts are a vision condition that is age-related in addition to resulting in blurry vision as the utmost common symptom. The treatment to get cataracts is generally surgically the removal of and replacement of the lens.
Ciliary Body
The ciliary body contains the ciliary lean muscle, which is responsible for controlling the imaginative and prescient vision accommodation reflex. The body is likewise an attachment point for any zonula threads and delivers aqueous fluid.
Optic Lack of feeling
The optic nerve enhances sending signals to different elements of the brain from the eye as a way to create images. It is made of about one million nerve posts and the nerves from both equal eyes are connected behind them so your left field of eye-sight is sent to the right hemisphere of the brain and corruption verse.
Macula
The imperfección consists of visual cells which might be closely packed resulting in excessive visual acuity, or excessive image resolution. These tissues are not as closely bundled around the macula as they are interior of your actual macula, but they command how well the peripheral vision works and is suitable for it to work properly. Deshonrar degeneration is a common eye disorder that occurs among the elderly and is separated into two classes: wet and dry. Soaked is more serious than dried out, but is also treatable along with FDA-approved drugs while dried out is not treatable and is the most typical.